Artificial Intelligence (AI) Policy
This AI policy is the comprehensive set of guidelines built to ensure the ethical, responsible, and compliant development, deployment, and use of AI technologies in alignment with the Agile Business Consortium’s organisational values.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools are transforming the way we work. They have the potential to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide valuable insights into our operations. However, AI tools also present new challenges regarding information security, data protection, bias mitigation, and ethical use. This policy guides Agile Business Consortium employees in the safe, secure, and responsible use of AI tools, especially when they share potentially sensitive organisational and customer information.
Please Note: In this entire document, where ‘employees’ are referenced, this applies to full-time contractual employees, contracted staff, and any other third parties that work with us.
Policy Statement
The Agile Business Consortium recognises that AI tools can harm our operations and customers. Therefore, we are committed to protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all organisational and customer data. This policy requires all employees of the Agile Business Consortium to use AI tools that are consistent with our security best practices and ethical standards.
Purpose and Scope
Coverage
This AI policy applies to all employees, contractors, and third-party partners involved in the design, development, procurement, deployment, use, or management of AI tools and systems within the organisation. It encompasses all AI technologies, tools, and applications used, regardless of whether they are developed in-house or acquired from external providers. The policy covers all aspects of AI system lifecycle management, including data collection, model training, testing, deployment, monitoring, and retirement. It also extends to any decision-making processes influenced by AI, ensuring compliance with legal, ethical, and organisational standards.
Current Application of AI
This AI policy applies to all AI platforms and tools utilised within the organisation as of 1st December 2024, including but not limited to:
-
ChatGPT and Generative AI Tools: This policy governs the use of ChatGPT and/or its competitors (such as Claude AI, Google’s Bard, Perplexity) and other generative AI tools (such as DALL-E, Scribe, Grammarly) used for communication, content generation, ideation, and problem-solving tasks.
-
Large Language Models (LLMs): All LLMs, whether developed in-house or sourced from external providers, are subject to this policy. This includes their use for tasks such as Natural Language Processing (NLP), conversational AI, summarisation, and more.
-
Plugins and Extensions: All plugins, integrations, or extensions that enhance or expand the capabilities of LLMs, such as tools enabling data analysis, task automation, or external Application Programming Interface (API) integrations.
-
Data-Enabled Tools: AI tools and systems that leverage organisational data for tasks such as predictive modelling, analytics, and personalised recommendations. This includes tools that process, analyse, or make decisions based on large datasets.
These tools and platforms must be used in accordance with the organisation’s guidelines on data privacy, ethical AI usage, and regulatory compliance, ensuring responsible deployment and adherence to the policy standards.
Future Application of AI
This policy also applies to the integration of future AI platforms, tools, and technologies within the organisation. As the AI landscape evolves, the Agile Business Consortium commits to assessing and incorporating new AI capabilities responsibly. Future integrations include:
-
Emerging AI Technologies: Any new AI models, frameworks, or platforms introduced to enhance operations, decision-making, or customer engagement must comply with the principles of transparency, fairness, and accountability outlined in this policy.
-
Third-Party and Vendor Tools: AI solutions sourced from external vendors, including updates to existing tools or new services, must undergo a risk assessment and review to ensure alignment with organisational standards (for example, existing tools such as Canva and HubSpot).
-
Custom-Built AI Solutions: AI systems developed internally to address specific business needs must adhere to this policy’s guidelines during their design, development, and deployment stages.
-
Integrated AI Ecosystems: Future cross-platform or multi-tool AI integrations must ensure interoperability, data security, and ethical compliance across all connected systems.
-
AI-Augmented Processes: Any enhancements to current workflows or processes using AI technologies must be documented, tested, and approved to ensure they align with organisational objectives and regulatory requirements.
By addressing future integrations in this policy, the Agile Business Consortium aims to maintain a proactive approach to technological advancements, fostering innovation while safeguarding ethical standards and operational integrity.
Ethics
Ethical Principles
The Agile Business Consortium is committed to upholding the following ethical principles in the development, deployment, and use of AI systems. These principles guide all AI-related activities to ensure fairness, accountability, and alignment with the organisation's values.
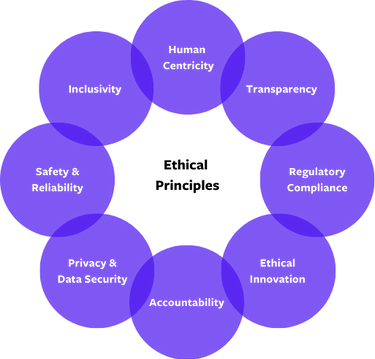
Human Centricity
AI systems should augment human capabilities and support operations rather than replace human judgement in critical areas. Human oversight and intervention will remain integral to AI processes. For example, using ChatGPT to create a blog draft or product brief would then need human intervention from the currect Subject Matter Expert (SME) or writer.
Transparency
When AI tools are used to create content, generate ideas, or support decision-making, it is crucial to clearly declare their involvement. Clear, understandable documentation and communication are required to build trust among stakeholders and users. This transparency ensures accountability, allowing others to understand the extent of the AI's contribution and verify the accuracy, reliability, and appropriateness of its outputs. Declaring AI use highlights its role as a support tool, ensuring that human expertise remains central to the process. It also promotes ethical standards and trust, both within the organisation and with external stakeholders. By openly acknowledging AI’s use, we demonstrate our commitment to responsible and fair practices while fostering a culture of transparency, collaboration and innovation.
Regulatory Compliance
All AI initiatives in the Agile Business Consortium will comply with the relevant laws, including those related to data protection, intellectual property, and algorithmic transparency. For example, the General Data Protect Regulations (GDPR) and Data Protection Act 2018 (DPA).
Ethical Innovation & Sustainability
The Agile Business Consortium supports innovation in AI while maintaining ethical boundaries. Emerging technologies must align with the organisation’s values. AI development and operations will aim to minimise environmental impact by adopting energy-efficient practices and technologies.
Accountability
Responsibility for AI systems lies with the organisation, its employees, and any third-party providers involved. Clear lines of accountability will be established to ensure ethical compliance and address any potential misuse or adverse outcomes.
Privacy and Data Security
All AI systems must respect user privacy and adhere to strict data protection standards. Data used for AI purposes will be collected, processed, and stored securely, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. Please refer back to the ‘Initial GDPR Training’ recording found in the Shared Area of SharePoint.
Safety and Reliability
AI systems must be rigorously tested to ensure they operate safely and reliably under diverse conditions. Continuous monitoring and improvement will be enforced to maintain their effectiveness and minimise risks.
Inclusivity
AI tools and systems will be designed to be accessible and inclusive, ensuring that they cater to a wide range of users and do not inadvertently marginalise any group. AI systems must be designed and operated to avoid bias and discrimination. This includes ensuring equitable outcomes across diverse user groups and continuously monitoring for unintended biases in data, algorithms, or decision-making processes.
By adhering to these ethical principles, the Agile Business Consortium ensures its AI initiatives contribute positively to its goals, stakeholders, and society at large.
Ethical Use of AI
What you must do:
Understand the limitations to AI
- Learn what AI can do and cannot do.
- Validate the output from AI, especially when it comes to creativity and critical thinking.
Always be transparent.
-
Disclose when you are using AI, it’s a great tool but only when used in the best way.
Prioritise Privacy and Consent
- Ensure you understand the impact of third-party apps using data and content that it interacts with.
- Comply with the relevant data protection laws (such as DPA and GDPR).
- Obtain explicit consent where AI is used to collect or process user data.
What you must NOT do:
Don’t use AI for Harmful Purposes
- Avoid applications that cause any sort of harm, this includes (and is not limited to) physical, psychological or societal harm. For example, be aware of deepfakes. and AI can create hallucinations or ‘fake content’
- Don’t mislead users. For example, don’t use AI to impersonate a real human to deceive others or claim they are sentient.
- Avoid using AI to automate processes where it is not necessary or is inappropriate to do so (for example, human interaction is key to the service).
Don’t deploy without testing
-
Never release anything either generated using AI applications or the applications themselves, without testing for safety, security and fairness.
Don’t Rely on AI Solely
-
Avoid using AI in all situations, especially in those situations that require human intuition, empathy or nuanced judgement.
Don’t Ignore Accessibility and Inclusivity
- Failing to address bias can lead to stereotypes and/or discrimination.
- Always consider the needs of all user demographics, to ignore this is exclusionary.
Data Governance
Key Legal Principles
This section of the policy reflects the Agile Business Consortium’s commitment to lawful and responsible AI usage in alignment with applicable legal and ethical standards as well as the legal and regulatory requirements.
The key legal principles include:
Data Privacy & Protection
The organisation will comply with relevant laws governing the collection, use, storage, and sharing of data. Appropriate measures will be taken to safeguard personal and sensitive information with adherenece to global, regional, and local data privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), or equivalent regulations.
Intellectual Property (IP) Rights
Compliance with intellectual property laws, including copyright, patent, and trade secret regulations. You must ensure AI-generated content respects third-party copyrights and does not infringe upon proprietary rights.
Fairness & Non-Discrimination
AI systems will be designed and monitored to ensure compliance with laws that prohibit discriminatory practices, ensuring equitable treatment for all individuals.
Transparency
The organisation will meet legal requirements to provide transparency in how AI systems operate, especially when they impact decisions that affect stakeholders.
Consumer Protection
All AI-powered products or services will adhere to applicable consumer protection laws, including those related to accurate representation and safe usage.
Accountability & Liability
The organisation will establish accountability for AI-related outcomes, ensuring compliance with legal standards for risk management and liability.
Sector-Specific Compliance
Where applicable, the organisation will adhere to legal frameworks specific to its industry or operational context, including those governing data, safety, and ethical AI use.
Ongoing Regulatory Monitoring
The organisation will monitor and adapt to evolving AI regulations, ensuring compliance with emerging legal standards and guidelines.
GDPR and DPA Compliance
This clause of the AI Policy outlines the obligations of the Agile Business Consortium and its employees are ensuring the use of AI systems complies with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Data Protection Act 2018 (DPA).
- All systems must process personal data only when a valid, lawful basis under GDPR is established (for example, consent, legitimate interest or contractual necessity). Employees must document the lawful basis for processing before deploying the use of AI applications.
- AI systems must only process the necessary data to achieve their intended purpose. Where possible, employees should always avoid the use of irrelevant or excessive personal data.
- Individuals must be informed when their personal data is processed by AI. This includes the purpose, legal basis and any automated decision-making involved.
- All systems must be designed and tested to prevent discriminatory outcomes or biases that could affect individuals’ rights under GDPR and DPA.
- AI systems must employ robust security measures to protect personal data from unauthorised access, loss or breach. This must be regularly assessed to ensure the security aligns with evolving threats.
- Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for AI systems that are likely to result in high risk to individuals’ rights. DPIAs must identify the risks and implement mitigation measures before deploying the use of AI systems.
Conclusion
Incorporating AI aligns with the Consortium's philosophy of leveraging innovative practices to deliver business value efficiently and adaptively. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement and helps organisations achieve agility in an increasingly digital world.
AI is transforming industries and redefining the way we work, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and growth. As the future of technology, AI has the potential to revolutionise decision-making, automate routine tasks, and unlock insights from data at a scale never before possible. However, with this potential comes significant responsibility. To fully embrace AI and harness its benefits, we must adopt robust policies that ensure its safe, ethical, and fair use. These policies guide how AI is developed, deployed, and monitored, mitigating risks such as bias, misuse, and security breaches. By balancing innovation with accountability, we can confidently leverage AI as a powerful tool to shape a better and more equitable future.
Artificial intelligence is not just a technological advancement; it is a transformative force shaping the future of work and society. Embracing AI allows us to unlock unprecedented efficiencies, drive innovation, and solve complex challenges across industries. As Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google, remarked, "AI is more profound than electricity or fire in terms of the impact it will have on our future." By adopting AI responsibly, we can enhance decision-making, automate repetitive tasks, and enable human creativity to flourish. To fully harness its potential, we must approach AI with openness and strategic planning, ensuring its integration is safe, ethical, and beneficial for all.
As industries adopt AI-driven solutions, the Consortium must incorporate AI in its frameworks to remain relevant and guide organisations in leveraging these technologies effectively within AgilePM methodologies .
Terminology
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The EU AI Act defines an "artificial intelligence (AI) system" as a machine-based system that:
- Operates with varying levels of autonomy
- Uses machine learning and/or logic- and knowledge based approaches
- Infers how to achieve a given set of human-defined objectives
- Generates outputs such as predictions, content, recommendations, or decisions
Application Programming Interface (API)
A set of functions and procedures allowing the creation of applications that access the features or data of an operating system, application, or other service.
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
A process that helps organisations identify and reduce the risks to individuals' privacy and data protection when processing personal data
Deepfakes
AI-generated or manipulated images, audio, or video content that resembles existing persons, objects, places, entities, or events.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI)
A subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that uses generative models to produce text, images, videos, or other forms of data.
Intellectual Property (IP)
A legal term for intangible creations of the human mind, such as inventions, designs, artistic works, and symbols. IP law protects the creators of these works and includes areas such as copyright, patents, and trademark law.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
A type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) model that uses machine learning to understand and generate
human language. LLMs are trained on massive amounts of data, such as text from the internet, andcan perform a variety of tasks.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
A type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that allows computers to understand, interpret, and manipulate human language.
References
Data Protection Act (2018)
General Data Protection Act (2016)
